This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful. More information in our Privacy Policy
Diagnostic magnetic nanoparticles
Magnetic calcium phosphate nanoparticles as contrast agent for diagnostic imaging
Principal investigators: Alessio Adamiano, Michele Iafisco, Monica Sandri, Anna Tampieri
Personnel involved: Silvia Panseri, Monica Montesi, Elisabetta Campodoni, Francesca Carella
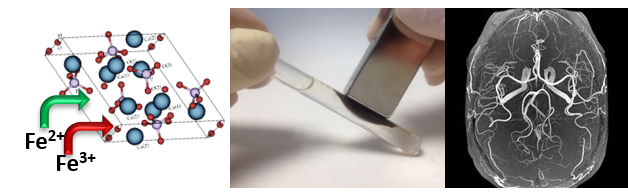
In the attempt to develop a fully biocompatible and biodegradable nanomaterial, ISTEC Biomaterials’ group has developed superparamagnetic nanoaprticles (FeHA) obtained by the substitution of Ca2+ ions with Fe2+ e Fe3+ in the lattice of hydroxyapatite. FeHA has a peculiar magnetic behaviour and display a mass magnetization at saturation (Ms) of 8.9 emu/gr at low fields (< 10 kOe) and no magnetic remanence at room temperature. Its ability of to work as contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was proved in vivo in the framework of a collaboration with the San Raffaele Hospital of Milan.
Finally, the possibility to localize FeHA nanoaprticles in vivo opens intriguing possibilities in some of the most advanced nanomedicine applications like:
1. Cell guiding and tracking. Stem cell therapy is one of the most promising areas for several disease treatments and regenerative medicine. Unfortunately, both systemic and local injection of cells have limitations accounting on the migration and retention of the cells to the injured organs. Magnetic cell targeting represents a promising approach to overcome these difficulties. At this purpose, we have recently demonstrated that FeHA nanoaprticles can be easily internalized by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) obtaining “magnetic cells” without sorting any negative effect on the cell viability and morphology.
2. FeHA can be employed simultaneously as nanocarriers for bioactive molecules and as diagnostic agent for the monitoring of therapies by MRI.
Equipment and processes
- Colloidal stability evaluation
- Magnetic susceptibility
- Chemical composition and crystallographic analysis
Main collaborations
- Università degli Studi di Milano
- Ospedale “San Raffaele” di Milano, Gruppi di Epatologia Sperimentale e Radiologia Clinica e Sperimentale
- BioEmission Technology Solutions
- SPIN-CNR
Projects
Publications & Patents
- Adamiano, Alessio, et al. “Magnetic calcium phosphates nanocomposites for the intracellular hyperthermia of cancers of bone and brain.” Nanomedicine 14.10 (2019): 1267-1289.
- Marrella, Alessandra, et al. “A combined low-frequency electromagnetic and fluidic stimulation for a controlled drug release from superparamagnetic calcium phosphate nanoparticles: potential application for cardiovascular diseases.” Journal of The Royal Society Interface 15.144 (2018): 20180236.
- Adamiano, Alessio, et al. “On the use of superparamagnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as an agent for magnetic and nuclear in vivo imaging.” Acta biomaterialia 73 (2018): 458-469.
- Adamiano, Alessio, Michele Iafisco, and Anna Tampieri. “Magnetic core-shell nanoparticles: Remote driving, hyperthermia, and controlled drug release.” Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics. Woodhead Publishing, 2018. 259-296.
- Iannotti, Vincenzo, et al. “Fe-doping-induced magnetism in nano-hydroxyapatites.” Inorganic chemistry 56.8 (2017): 4446-4458.
